New model reconciles the Moon's Earth-like composition with the giant impact theory of formation
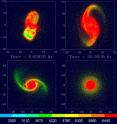
The giant impact believed to have formed the Earth-Moon system has long been accepted as canon. However, a major challenge to the theory has been that Earth and Moon have identical oxygen isotope compositions, even though earlier impact models indicated they should differ substantially. In a paper published October 17 in the journal Science online, a new model by Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), motivated by accompanying work by others on the early dynamical history of the Moon, accounts for this similarity in composition while also yielding an appropriate mass for Earth and the Moon. In the giant impact scenario, the Moon forms from debris ejected into an Earth-orbiting disk by the collision of a smaller proto-planet with the early Earth. Earlier models found that most or much of the disk material would have originated from the Mars-sized impacting body, whose composition likely would have differed substantially from that of Earth.
The new models developed by Dr. Robin M. Canup, an associate vice president in the SwRI Space Science and Engineering Division, and funded by the NASA Lunar Science Institute, involve much larger impactors than were previously considered. In the new simulations, both the impactor and the target are of comparable mass, with each containing about 4 to 5 times the mass of Mars. The near symmetry of the collision causes the disk's composition to be extremely similar to that of the final planet's mantle over a relatively broad range of impact angles and speeds, consistent with the Earth-Moon compositional similarities.
The new impacts produce an Earth that is rotating 2 to 2.5 times faster than implied by the current angular momentum of the Earth-Moon system, which is contained in both Earth's rotation and the Moon's orbit. However, in an accompanying paper in Science, Dr. Matija Ćuk, SETI Institute, and Dr. Sarah T. Stewart, Harvard University, show that a resonant interaction between the early Moon and the Sun -- known as the evection resonance -- could have decreased the angular momentum of the Earth-Moon system by this amount soon after the Moon-forming impact.
"By allowing for a much higher initial angular momentum for the Earth-Moon system, the Ćuk and Stewart work allows for impacts that for the first time can directly produce an appropriately massive disk with a composition equal to that of the planet's mantle," says Canup.
In addition to the impacts identified in Canup's paper, Ćuk and Stewart show that impacts involving a much smaller, high-velocity impactor colliding into a target that is rotating very rapidly due to a prior impact can also produce a disk-planet system with similar compositions.
"The ultimate likelihood of each impact scenario will need to be assessed by improved models of terrestrial planet formation, as well as by a better understanding of the conditions required for the evection resonance mechanism," adds Canup.
Canup used smoothed-particle hydrodynamics (SPH) to simulate the colliding planetary objects using 300,000 discrete particles whose individual thermodynamic and gravitational interactions were tracked with time.
Source: Southwest Research Institute
Articles on the same topic
- Proof at last: Moon was created in giant smashupWed, 17 Oct 2012, 18:08:54 UTC
Other sources
- Reports put new spin on story of moon's creationfrom LA Times - ScienceThu, 18 Oct 2012, 0:30:27 UTC
- Moon-forming impact theory rescuedfrom News @ NatureWed, 17 Oct 2012, 21:00:42 UTC
- New model reconciles the Moon's Earth-like composition with the giant impact theory of formationfrom Science DailyWed, 17 Oct 2012, 20:00:38 UTC
- Separated after birthfrom Harvard ScienceWed, 17 Oct 2012, 19:50:20 UTC
- Huge Moon-Forming Collision Theory Gets New Spinfrom Space.comWed, 17 Oct 2012, 19:31:18 UTC
- Updated Theory: A Huge Chunk Of Earth, Blasted Away In A Collision, Is Now The Moonfrom PopSciWed, 17 Oct 2012, 19:31:16 UTC
- New model reconciles the Moon's Earth-like composition with the giant impact theory of formationfrom PhysorgWed, 17 Oct 2012, 19:01:06 UTC
- Massive Planetary Collision May Have Zapped Key Elements from Moonfrom Newswise - ScinewsWed, 17 Oct 2012, 19:00:38 UTC
- Study finds proof of moon's violent birth in zincfrom CBSNews - ScienceWed, 17 Oct 2012, 18:30:33 UTC
- Proof of Moon's Birth in Giant Impact Found in Zinc: Studyfrom Space.comWed, 17 Oct 2012, 18:01:17 UTC
- Moon was created in giant smashup; Vaporization of impactor left signature in tiny excess of heavier form of zincfrom Science DailyWed, 17 Oct 2012, 18:01:10 UTC
- Massive planetary collision may have zapped key elements from moonfrom Science DailyWed, 17 Oct 2012, 18:01:07 UTC
- New study proves Moon was created in massive planetary collisionfrom PhysorgWed, 17 Oct 2012, 17:02:10 UTC