The proteins that domesticated our genomes
EPFL scientists have carried out a genomic and evolutionary study of a large and enigmatic family of human proteins, to demonstrate that it is responsible for harnessing the millions of transposable elements in the human genome. The work reveals the...
Study links altered brain chemistry, behavioral impairments in fish exposed to elevated CO2
 Study Links Altered Brain Chemistry, Behavioral Impairments in Fish Exposed to Elevated CO2 Research team studied damselfish behavior and physiology under ocean acidification conditions predicted for year 2300
Study Links Altered Brain Chemistry, Behavioral Impairments in Fish Exposed to Elevated CO2 Research team studied damselfish behavior and physiology under ocean acidification conditions predicted for year 2300
Water helps assembly of biofibers that could capture sunlight
 When it comes to water, some materials have a split personality - and some of these materials could hold the key to new ways of harnessing solar energy.
When it comes to water, some materials have a split personality - and some of these materials could hold the key to new ways of harnessing solar energy.
Astronomers observe star reborn in a flash
 An international team of astronomers using Hubble have been able to
study stellar evolution in real time. Over a period of 30 years
dramatic increases in the temperature of the...
An international team of astronomers using Hubble have been able to
study stellar evolution in real time. Over a period of 30 years
dramatic increases in the temperature of the...
NASA's Aqua satellite sees Super Typhoon Meranti approaching Taiwan, Philippines
 NASA's Aqua satellite provided a visible image of Super Typhoon Meranti as it continued to move toward Taiwan and the northern Philippines.
NASA's Aqua satellite provided a visible image of Super Typhoon Meranti as it continued to move toward Taiwan and the northern Philippines.
Manipulation of liquid crystals could help control drug-delivery process
Liquid crystals are strange substances, both fish and fowl. They can flow like a liquid, but have the orderly molecular structure of a crystalline solid. And that internal structure can...
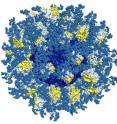
First accurate simulation of a virus invading a cell
For the first time, scientists know what happens to a virus' shape when it invades a host cell, thanks to an experiment by researchers at Penn State College of Medicine...
Chemists offer enhanced 3-D look inside batteries
 A team of chemists has developed a method to yield highly detailed,
three-dimensional images of the insides of batteries. The
technique, based on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), offers an enhanced...
A team of chemists has developed a method to yield highly detailed,
three-dimensional images of the insides of batteries. The
technique, based on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), offers an enhanced...
Trees recognize roe deer by saliva
 In spring, the young, delicate shoots in the forest light up,
bright and May green. The buds and shoots are the future of the
forests as they allow young trees...
In spring, the young, delicate shoots in the forest light up,
bright and May green. The buds and shoots are the future of the
forests as they allow young trees...
App vs. website: Which best protects your privacy?
 That's the question that Northeastern researchers, led by
assistant professor David Choffnes, ask in new research that
explores how free app- and web- based services on Android and iOS mobile...
That's the question that Northeastern researchers, led by
assistant professor David Choffnes, ask in new research that
explores how free app- and web- based services on Android and iOS mobile...
New laser provides ultra-precise tool for scientists probing the secrets of the universe
Researchers have developed a new laser that makes it possible to measure electron transition energies in small atoms and molecules with unprecedented precision. The instrument will help scientists test one...
Land-based food not nutritionally sufficient for wild polar bears, according to new study
A study, by San Diego Zoo Global conservationists, released this week (Sept. 12, 2016) is shedding new light on how scientists evaluate polar bear diet and weight loss during their fasting season. On average, a polar bear loses up to...
Experts anticipate significant continued reductions in wind energy costs
 Technology advancements are expected to continue to drive down the
cost of wind energy, according to a survey of the world's foremost
wind power experts led by Lawrence Berkeley National...
Technology advancements are expected to continue to drive down the
cost of wind energy, according to a survey of the world's foremost
wind power experts led by Lawrence Berkeley National...
Westerly winds have blown across central Asia for at least 42 million years
 The gusting westerly winds that dominate the climate in central
Asia, setting the pattern of dryness and location of central Asian
deserts, have blown mostly unchanged for 42 million years....
The gusting westerly winds that dominate the climate in central
Asia, setting the pattern of dryness and location of central Asian
deserts, have blown mostly unchanged for 42 million years....
Killing superbugs with star-shaped polymers, not antibiotics
 The study, published today in Nature Microbiology, holds promise for a new treatment method against antibiotic-resistant bacteria (commonly known as superbugs).
The study, published today in Nature Microbiology, holds promise for a new treatment method against antibiotic-resistant bacteria (commonly known as superbugs).
Language delivers fourfold speedups on big-data problems
In today's computer chips, memory management is based on what computer scientists call the principle of locality: If a program needs a chunk of data stored at some memory location,...
Termination of lethal arrhythmia with light
 A research team from the University of Bonn has succeeded for the
first time in using light stimuli to stop life-threatening cardiac
arrhythmia in mouse hearts. Furthermore, as shown in...
A research team from the University of Bonn has succeeded for the
first time in using light stimuli to stop life-threatening cardiac
arrhythmia in mouse hearts. Furthermore, as shown in...
Explaining why the universe can be transparent
 Two papers published by an assistant professor at the University of California, Riverside and several collaborators explain why the universe has enough energy to become transparent.
Two papers published by an assistant professor at the University of California, Riverside and several collaborators explain why the universe has enough energy to become transparent.
NASA's THEMIS sees Auroras move to the rhythm of Earth's magnetic field
 The majestic auroras have captivated humans for thousands of years,
but their nature -- the fact that the lights are electromagnetic
and respond to solar activity -- was only realized...
The majestic auroras have captivated humans for thousands of years,
but their nature -- the fact that the lights are electromagnetic
and respond to solar activity -- was only realized...
Historical analysis examines sugar industry role in heart disease research
Using archival documents, a new report published online by JAMA Internal Medicine examines the sugar industry's role in coronary heart disease research and suggests the industry sponsored research to influence...
Study reveals how ionising radiation damages DNA and causes cancer
For the first time, researchers from the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute and their collaborators have been able to identify in human cancers two characteristic patterns of DNA damage caused by...
NASA sees formation of Central Atlantic Tropical Storm Ian
The low pressure area known as System 94L developed into Tropical Storm Ian on Sept. 14. NOAA's GOES-East satellite data was made into an animation that showed the...
Check out our next project, Biology.Net
Science News in Images
Latest Science Newsletter
Get the latest and most popular science news articles of the week in your Inbox! It's free!Breaking science news from the newsfeed
- A New Era for Physics? With Creation of New Form of Matter, a Time Crystal, It Just Might Be
- Old stardust in young galaxy sheds light on the first stars
- Rock art discovered in "Dark Ages" tomb in Israel
- Dental plaque DNA shows Neandertals used ‘aspirin’
- February's Warmth, Brought to You by Climate Change
- Neanderthal Used Penicillin and Aspirin
- Malta's Famous 'Azure Window' Collapses
- Neanderthals Munched on 'Aspirin' and Woolly Rhinos
- Researchers identify therapy that shrinks tumors in patients with multiple myeloma
- Casts of 'The Godfather,' 'Reservoir Dogs' to reunite at Tribeca
- Dampened immunity during pregnancy promotes evolution of more virulent flu
- New Enzyme-Like Tool Lets Chemists Modify Hard-to-Reach Spots on Drug Molecules
- Aboriginal Hair Shows 50,000 Years Connection to Country
- Researchers find neurological link between religious experiences and epilepsy
- Silk Road evolved as 'grass-routes' movement
- Researchers create new material to regrow bone
- Controversial 'liberation therapy' fails to treat multiple sclerosis
- Super-sized memory is trainable and long lasting
- High folic acid level in pregnancy may decrease high blood pressure in children
- Photos: 2,000-Year-Old Roman Road and Coins Discovered in Israel
- Republican governors complain about GOP health care plan
- Blue Origin's Giant New Glenn Rocket in Pictures
- Hepatitis C testing still low for baby boomers, study says
- Chemists create molecular 'leaf' that collects and stores solar power without solar panels
- Uncovering new relationships, organizational principles in protein interaction networks
- Researchers take big step forward in nanotech-based drugs
- In battle for real estate, a disordered protein wins out
- Ciara, Russell Wilson cause stir with nearly nude family photo
Earth & Climate
- One-tenth of the world's wilderness lost in 2 decades
- A tenth of the world's wilderness lost since the 1990s
- Study: A tenth of the world's wilderness lost since the 1990s
- NIST and Navy tests suggest telecom networks could back up GPS time signals
- Study finds earthquakes can trigger near-instantaneous aftershocks on different faults
Health & Medicine
- New study finds rate of injuries among youth soccer players doubled
- Prevention programs significantly reduce ankle injuries in soccer athletes
- How to fight drug-resistant bacteria
- Antimicrobial chemicals found with antibiotic-resistance genes in indoor dust
- Antibacterial ingredients in indoor dust could contribute to antibiotic resistance
Mathematics & Economics
- Team of robots learns to work together, without colliding
- New service improves cloud storage usage on mobile devices
- Beat the stock market by satisfying customers
- Researchers find vulnerabilities in iPhone, iPad operating system
- Louisiana Tech University uses underground radar to locate post-Katrina damage
Paleontology & Archaeology
- Researchers name a new species of reptile from 212 million years ago
- 13th century Maya codex, long shrouded in controversy, proves genuine
- Similarities found between how ancient and modern fish survived youth
- Genetics of African KhoeSan populations maps to Kalahari Desert geography
- Browsing antelope turned ancient African forests into grassy savanna ecosystems
Psychology & Sociology
- Posting personal experiences on social media may help you remember them in the future
- Life after Fitbit: Appealing to those who feel guilty vs. free
- Pet therapy can combat homesickness
- UBC research could help local governments plan together
- Link between weather and chronic pain is emerging through innovative smartphone research