Marine scientists use JeDI to create world's first global jellyfish database
An international study, led by the University of Southampton, has led to the creation of the world's first global database of jellyfish records to map jellyfish populations in the oceans. The debate regarding future trends, and subsequent ecological, biogeochemical and societal impacts, of jellyfish and jellyfish blooms in a changing ocean is hampered by a lack of information about jellyfish biomass and distribution from which to compare.
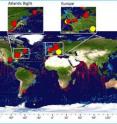
To address this knowledge gap, scientists used the Jellyfish Database Initiative, or JeDI, to map jellyfish biomass in the upper 200m of the world's oceans and explore the underlying environmental causes driving the observed patterns of distribution.
"The successful development of this first global‐scale database of jellyfish records by the Global Jellyfish Group was due, in large part, to the incredible generosity of members in the international jellyfish research and wider scientific communities," says lead author of the study Dr Cathy Lucas, a marine biologist from the University of Southampton.
"With this resource, anyone can use JeDI to address questions about the spatial and temporal extent of jellyfish populations at local, regional and global scales, and the potential implications for ecosystem services and biogeochemical processes," adds Dr Rob Condon of the University of North Carolina Wilmington in the USA.
Using data from JeDI, the authors were able to show that jellyfish and other gelatinous zooplankton are present throughout the world's oceans, with the greatest concentrations in the mid-latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere. In the North Atlantic Ocean, dissolved oxygen and sea surface temperature were found to be the principal drivers of jellyfish biomass distribution.
The spatial analysis carried out by the researchers is an essential first step in the establishment of a consistent database of gelatinous presence from which future trends can be assessed and hypotheses tested, particularly those relating multiple regional and global drivers of jellyfish biomass. It complements the findings of a 2013 study, led by Dr Condon, in which global jellyfish populations were shown to exhibit fluctuations over multidecadal time-scales centred round a baseline. "If jellyfish biomass does increase in the future, particularly in the Northern Hemisphere, this may influence the abundance and biodiversity of zooplankton and phytoplankton, having a knock-on effect on ecosystem functioning, biogeochemical cycling and fish biomass," says Dr Condon.
The Jellyfish Database Initiative, or JeDI, is the first scientifically-coordinated global-scale database of jellyfish records, and currently holds over 476,000 data items on jellyfish and other gelatinous taxa. JeDI has been designed as an open‐access database for all researchers, media and public to use as a current and future research tool and a data hub for general information on jellyfish populations. It is housed at the National Center for Ecological Analysis and Synthesis (NCEAS) USA, a cross-discipline ecological and data synthesis research centre affiliated with the University of California, Santa Barbara.
The continued development of JeDI and a re-analysis several decades from now will enable science to determine whether jellyfish biomass and distribution alter as a result of anthropogenic climate change.
Source: University of Southampton
Other sources
- Marine scientists create world’s first global jellyfish databasefrom Science DailyFri, 16 May 2014, 0:03:00 UTC
- Marine scientists use JeDI to create world's first global jellyfish databasefrom PhysorgThu, 15 May 2014, 15:30:59 UTC
- Study shows jellyfish blooms can be predicted by calm trade windsfrom PhysorgWed, 14 May 2014, 14:01:46 UTC
- The Beautiful New Jellyfish Identified in the Gulf of Venicefrom Live ScienceWed, 14 May 2014, 5:31:14 UTC
- Forecast for deadly jellyfish bloomsfrom BBC News: Science & NatureWed, 14 May 2014, 1:20:31 UTC
- Deadly Jellyfish Blooms Predictable, New Study Findsfrom Live ScienceTue, 13 May 2014, 23:20:40 UTC
- ScienceShot: Wind Patterns Forecast Jellyfish Attacksfrom Science NOWTue, 13 May 2014, 23:20:07 UTC